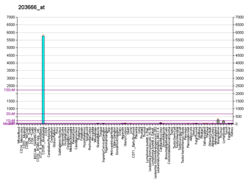
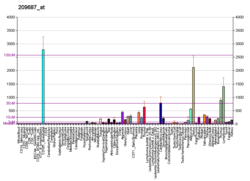
CXCL12
| CXCL12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
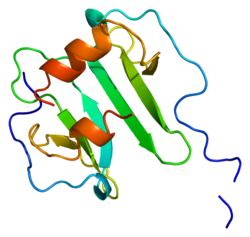 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure de la protéine CXCL12. Basé sur l'identifiant PDB 1a15. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CXCL12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IDs externes | OMIM: 600835 MGI: 103556 HomoloGene: 128606 GeneCards: CXCL12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Le CXCL12, appelée également stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1), est une protéine chimiokine de type CXC.
Rôles
Ses récepteurs sont le CXCR4 et le CXCR7[5].
Il intervient dans les interactions cellulaires dans le système immunitaire.
Il joue un rôle dans la migration cellulaire dans le système nerveux central en cours de développement[5]. Il protège ainsi les nouveaux neurones contre l'apoptose en stimulant l'expression de la protéine Rb[6] et en inhibant le récepteur de la NMDA (acide N-méthyl-D-aspartique)[7]. Sa propre expression est augmenté en cas d'accident vasculaire cérébral au niveau de la partie ischémiée du cerveau, contribuant à la migration de cellules progénitrices à ce niveau[8]. Il permet, par ailleurs, de moduler la neurotransmission et les interactions avec les cellules gliales[9].
La chaîne lourde de la ferritine interagit cependant avec le CXCR4, ce qui altère le signal induit par le CXCL12[10] et serait l'un des mécanismes suspecté de l'atteinte des fonctions supérieures lors du SIDA[11].
Notes et références
- ↑ a b et c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000107562 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ a b et c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000061353 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour l'Homme », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ « Publications PubMed pour la Souris », sur National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine
- ↑ a et b Tiveron MC, Cremer H, CXCL12/CXCR4 signalling in neuronal cell migration, Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2008;18:237–244
- ↑ Khan MZ, Brandimarti R, Shimizu S, Nicolai J, Crowe E, Meucci O, The chemokine CXCL12 promotes survival of postmitotic neurons by regulating Rb protein, Cell Death Differ, 2008;15:1663–1672
- ↑ Nicolai J, Burbassi S, Rubin J, Meucci O, CXCL12 inhibits expression of the NMDA receptor’s NR2B subunit through a histone deacetylase-dependent pathway contributing to neuronal survival, Cell Death Dis, 2010;1:e33
- ↑ Robin AM, Zhang ZG, Wang L et al. Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha mediates neural progenitor cell motility after focal cerebral ischemia, J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2006;26:125–134
- ↑ Li M, Ransohoff RM, Multiple roles of chemokine CXCL12 in the central nervous system: a migration from immunology to neurobiology, Prog Neurobiol, 2008;84:116–131
- ↑ Li R, Luo C, Mines M, Zhang J, Fan GH, Chemokine CXCL12 induces binding of ferritin heavy chain to the chemokine receptor CXCR4, alters CXCR4 signaling, and induces phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of ferritin heavy chain, J Biol Chem, 2006;281:37616–37627
- ↑ Pitcher J, Abt A, Myers J et al. Neuronal ferritin heavy chain and drug abuse affect HIV-associated cognitive dysfunction, J Clin Investig, 2014
 Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire
Portail de la biologie cellulaire et moléculaire  Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine