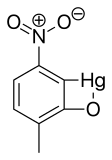
Nitromersol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 5-Methyl-2-nitro-7-oxa-8-mercurabicyclo[4.2.0]octa-1(6),2,4-triene | |
| Other names Metaphen; 6-Methyl-3-nitrobenzoxamercurete; 4-Nitro-5-hydroxymercuriorthocresol | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.648 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C7H5HgNO3 |
| Molar mass | 351.713 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | moderately toxic |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Nitromersol (metaphen) is a mercury-containing organic compound that is primarily used as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is a brown-yellow solid that has no odor or taste, does not irritate the skin or mucous membranes, and has no impact on rubber or metallic instruments, including surgical and dental tools.[1]
This compound is a confirmed animal carcinogen. It can emit toxic fumes of NOx and mercury vapor when heated.[2] In 1998, use of nitromersol (and other mercury-containing products) as OTC first-aid antiseptics and products for diaper rash and vaginal contraceptives was disallowed by the FDA.[3] Nitromersol can cause hypersensitivity reactions.[4]
It is still in use as a preservative for vaccines and antitoxins.[examples needed]
See also
- Thiomersal – Organomercury antiseptic and antifungal agent
- Phenylmercuric nitrate - an organomercury compound with powerful antiseptic and antifungal effects
References
- ^ Hospital formulary and compendium of useful information. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. 1941. p. 113. Retrieved 2011-04-08.
- ^ Lewis, Richard J. (2008). Hazardous chemicals desk reference. Wiley-Interscience. p. 1018. ISBN 978-0-470-18024-2. Retrieved 2011-04-08.
- ^ Remington: the science and practice of pharmacy. Medicine Series. Vol. 1 (21st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2005. p. 369. ISBN 0-7817-4673-6.
- ^ Trevor, Anthony J.; Katzung, Bertram G.; Masters, Susan B. (2007). Katzung & Trevor's pharmacology: examination & board review. Lange Basic Science (8th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 420. ISBN 978-0-07-148869-3.
- v
- t
- e
- Mercuric amidochloride
- Phenylmercuric borate
- Mercuric chloride
- Merbromin
- Nitromersol
- Thiomersal
- Mercuric iodide
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III












