Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| ATP5F1C |
|---|
 |
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | ATP5F1C, ATP5C, ATP5CL1, ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, gamma polypeptide 1, ATP5C1, ATP synthase F1 subunit gamma |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 108729; MGI: 1261437; HomoloGene: 3792; GeneCards: ATP5F1C; OMA:ATP5F1C - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 10p14 | Start | 7,788,147 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 7,807,815 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 2|2 A1 | Start | 10,060,827 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 10,085,321 bp[2] |
|---|
|
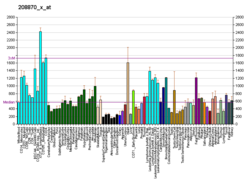
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - right ventricle
- myocardium of left ventricle
- vena cava
- triceps brachii muscle
- body of tongue
- biceps brachii
- deltoid muscle
- right adrenal gland
- right adrenal cortex
- glutes
|
| | Top expressed in | - myocardium of ventricle
- cardiac muscles
- cardiac muscle tissue of left ventricle
- thoracic diaphragm
- extraocular muscle
- masseter muscle
- plantaris muscle
- triceps surae
- interventricular septum
- quadriceps femoris muscle
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 

 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism
- transmembrane transporter activity
- ATPase activity
- RNA binding
- proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism
| | Cellular component | - mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex
- membrane
- myelin sheath
- mitochondrial matrix
- mitochondrion
- mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic sector F(1)
- mitochondrial inner membrane
- proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic core F(1)
- extracellular exosome
| | Biological process | - mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport
- ion transport
- oxidative phosphorylation
- ATP synthesis coupled proton transport
- ATP biosynthetic process
- cristae formation
- transport
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001001973
NM_005174
NM_001320886 |
| |
|---|
NM_001112738
NM_020615
NM_001374641 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001001973
NP_001307815
NP_005165 |
| |
|---|
NP_001106209
NP_065640
NP_001361570 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 10: 7.79 – 7.81 Mb | Chr 2: 10.06 – 10.09 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
The human ATP5F1C gene encodes the gamma subunit of an enzyme called mitochondrial ATP synthase.[5][6][7]
This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, F0, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The proton channel consists of three main subunits (a, b, c). This gene encodes the gamma subunit of the catalytic core. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. This gene also has a pseudogene on chromosome 14.[7]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000165629 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025781 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Jabs EW, Thomas PJ, Bernstein M, Coss C, Ferreira GC, Pedersen PL (Jun 1994). "Chromosomal localization of genes required for the terminal steps of oxidative metabolism: alpha and gamma subunits of ATP synthase and the phosphate carrier". Hum Genet. 93 (5): 600–2. doi:10.1007/bf00202832. PMID 8168843. S2CID 39597611.
- ^ Matsuda C, Endo H, Ohta S, Kagawa Y (Dec 1993). "Gene structure of human mitochondrial ATP synthase gamma-subunit. Tissue specificity produced by alternative RNA splicing". J Biol Chem. 268 (33): 24950–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)74556-6. PMID 8227057.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ATP5F1C ATP synthase F1 subunit gamma".
External links
- Human ATP5F1C genome location and ATP5F1C gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q91VR2 (ATP synthase subunit gamma, mitochondrial) at the PDBe-KB.
Further reading
- Yoshida M, Muneyuki E, Hisabori T (2001). "ATP synthase--a marvellous rotary engine of the cell". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2 (9): 669–77. doi:10.1038/35089509. PMID 11533724. S2CID 3926411.
- Abrahams JP, Leslie AG, Lutter R, Walker JE (1994). "Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria". Nature. 370 (6491): 621–8. Bibcode:1994Natur.370..621A. doi:10.1038/370621a0. PMID 8065448. S2CID 4275221.
- Elston T, Wang H, Oster G (1998). "Energy transduction in ATP synthase". Nature. 391 (6666): 510–3. Bibcode:1998Natur.391..510E. doi:10.1038/35185. PMID 9461222. S2CID 4406161.
- Yasuda R, Noji H, Kinosita K, Yoshida M (1998). "F1-ATPase is a highly efficient molecular motor that rotates with discrete 120 degree steps". Cell. 93 (7): 1117–24. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81456-7. PMID 9657145. S2CID 14106130.
- Wang H, Oster G (1998). "Energy transduction in the F1 motor of ATP synthase". Nature. 396 (6708): 279–82. Bibcode:1998Natur.396..279W. doi:10.1038/24409. PMID 9834036. S2CID 4424498.
- Hayakawa M, Sakashita E, Ueno E, Tominaga S, Hamamoto T, Kagawa Y, et al. (2002). "Muscle-specific exonic splicing silencer for exon exclusion in human ATP synthase gamma-subunit pre-mRNA". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (9): 6974–84. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110138200. PMID 11744705.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, Derge JG, Klausner RD, Collins FS, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Cross RL (2004). "Molecular motors: turning the ATP motor". Nature. 427 (6973): 407–8. Bibcode:2004Natur.427..407C. doi:10.1038/427407b. PMID 14749816. S2CID 52819856.
- Itoh H, Takahashi A, Adachi K, Noji H, Yasuda R, Yoshida M, et al. (2004). "Mechanically driven ATP synthesis by F1-ATPase". Nature. 427 (6973): 465–8. doi:10.1038/nature02212. PMID 14749837. S2CID 4428646.
- Deloukas P, Earthrowl ME, Grafham DV, Rubenfield M, French L, Steward CA, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 10". Nature. 429 (6990): 375–81. Bibcode:2004Natur.429..375D. doi:10.1038/nature02462. PMID 15164054.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, Shenmen CM, Grouse LH, Schuler G, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, Haenig C, Brembeck FH, Goehler H, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0. PMID 16169070. S2CID 8235923.
- Fukumura K, Kato A, Jin Y, Ideue T, Hirose T, Kataoka N, et al. (2007). "Tissue-specific splicing regulator Fox-1 induces exon skipping by interfering E complex formation on the downstream intron of human F1γ gene". Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (16): 5303–11. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm569. PMC 2018636. PMID 17686786.
PDB gallery
-
1bmf: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE -
1cow: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH AUROVERTIN B -
1e1q: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE AT 100K -
1e1r: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY MG2+ADP AND ALUMINIUM FLUORIDE -
1e79: BOVINE F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY DCCD (DICYCLOHEXYLCARBODIIMIDE) -
1efr: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTIC EFRAPEPTIN -
1h8e: (ADP.ALF4)2(ADP.SO4) BOVINE F1-ATPASE (ALL THREE CATALYTIC SITES OCCUPIED) -
1h8h: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE PRESENCE OF 5MM AMPPNP -
1mab: RAT LIVER F1-ATPASE -
1nbm: THE STRUCTURE OF BOVINE F1-ATPASE COVALENTLY INHIBITED WITH 4-CHLORO-7-NITROBENZOFURAZAN -
1ohh: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR PROTEIN IF1 -
1w0j: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE -
1w0k: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE -
2ck3: AZIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE -
2f43: Rat liver F1-ATPase -
2jdi: GROUND STATE STRUCTURE OF F1-ATPASE FROM BOVINE HEART MITOCHONDRIA (BOVINE F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE ABSENCE OF AZIDE) |
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 10 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |

 1bmf: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE
1bmf: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE 1cow: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH AUROVERTIN B
1cow: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH AUROVERTIN B 1e1q: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE AT 100K
1e1q: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE AT 100K 1e1r: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY MG2+ADP AND ALUMINIUM FLUORIDE
1e1r: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY MG2+ADP AND ALUMINIUM FLUORIDE 1e79: BOVINE F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY DCCD (DICYCLOHEXYLCARBODIIMIDE)
1e79: BOVINE F1-ATPASE INHIBITED BY DCCD (DICYCLOHEXYLCARBODIIMIDE) 1efr: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTIC EFRAPEPTIN
1efr: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE PEPTIDE ANTIBIOTIC EFRAPEPTIN 1h8e: (ADP.ALF4)2(ADP.SO4) BOVINE F1-ATPASE (ALL THREE CATALYTIC SITES OCCUPIED)
1h8e: (ADP.ALF4)2(ADP.SO4) BOVINE F1-ATPASE (ALL THREE CATALYTIC SITES OCCUPIED) 1h8h: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE PRESENCE OF 5MM AMPPNP
1h8h: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE PRESENCE OF 5MM AMPPNP 1mab: RAT LIVER F1-ATPASE
1mab: RAT LIVER F1-ATPASE 1nbm: THE STRUCTURE OF BOVINE F1-ATPASE COVALENTLY INHIBITED WITH 4-CHLORO-7-NITROBENZOFURAZAN
1nbm: THE STRUCTURE OF BOVINE F1-ATPASE COVALENTLY INHIBITED WITH 4-CHLORO-7-NITROBENZOFURAZAN 1ohh: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR PROTEIN IF1
1ohh: BOVINE MITOCHONDRIAL F1-ATPASE COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR PROTEIN IF1 1w0j: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE
1w0j: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE 1w0k: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE
1w0k: BERYLLIUM FLUORIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE 2ck3: AZIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE
2ck3: AZIDE INHIBITED BOVINE F1-ATPASE 2f43: Rat liver F1-ATPase
2f43: Rat liver F1-ATPase 2jdi: GROUND STATE STRUCTURE OF F1-ATPASE FROM BOVINE HEART MITOCHONDRIA (BOVINE F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE ABSENCE OF AZIDE)
2jdi: GROUND STATE STRUCTURE OF F1-ATPASE FROM BOVINE HEART MITOCHONDRIA (BOVINE F1-ATPASE CRYSTALLISED IN THE ABSENCE OF AZIDE)



































